Appendix 3: http access to the IFB cloud
How to access to a machine deployed in the IFB core cloud ?¶
The problem¶
All virtual machines deployed in the IFB core are located in a subnetwork whose access is limited to
- the port 22, for ssh connections
- the port 443, for https (web) connections.
Note that the port 80 is not open, precluding connection through the "insecure" http port of your web Galaxy server.
Accessing a web server running on a virtual instance through https (443) requires
that each machine has declared its own SSL certificate and most preferably owns a unique
domain name, in the form of mymachine.ifb.fr.
Although there are turnarounds for generating self-signed SSL certificate for cloud instances,
this implies manipulations which are beyond the scope on this training for beginners.
There is a least 2 ways for circumventing the https limitation for this training.
1. Running a SOCKS proxy on your local machine¶
A. using your remote virtual machine
Type in a terminal session (and leave it alive):
ORB. using another virtual machine of the IFB cloud
Type in a terminal session (and leave it alive):
ssh -i .ssh/ifbsocks -D 9900 ubuntu@<communicated.ifb.ip.address> # with the ifbsocks private key which you will be given
THEN
- open your system network settings
- go to your system proxy settings
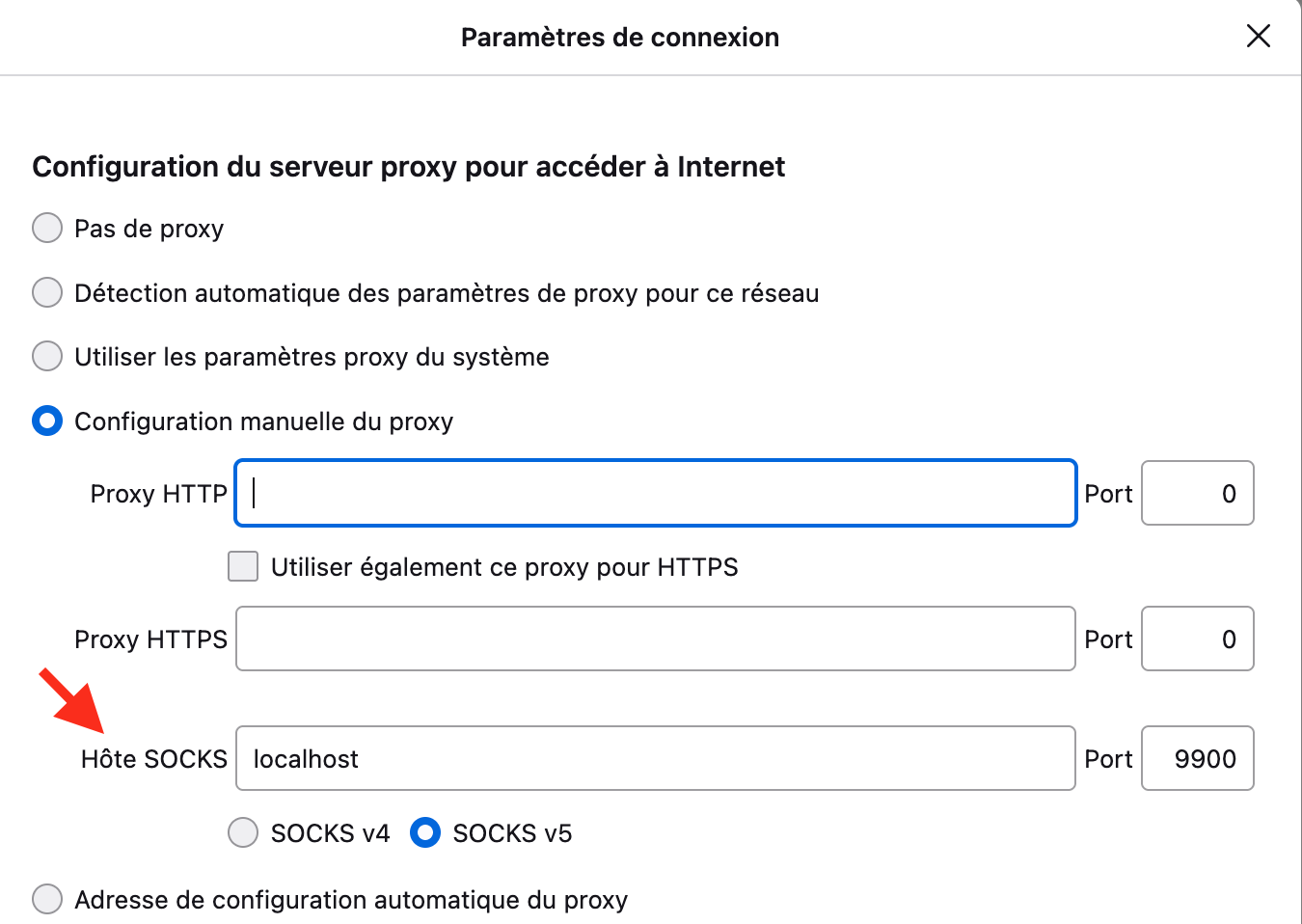
- Check the box for SOCKS Proxy (v4 or v5)
- in the field for the Server Proxy SOCKS address, enter
localhost - in the field for the Server Proxy SOCKS port, enter
9900
you can also set your socks proxy settings directly in Firefox (but not in Chrome)
Go to about:preferences#general in Firefox and click "Parameters at the very bottom of the page":
From this point
You should be able to access directly to your cloud Galaxy server by typing
http://<IFB.IP.your.server>
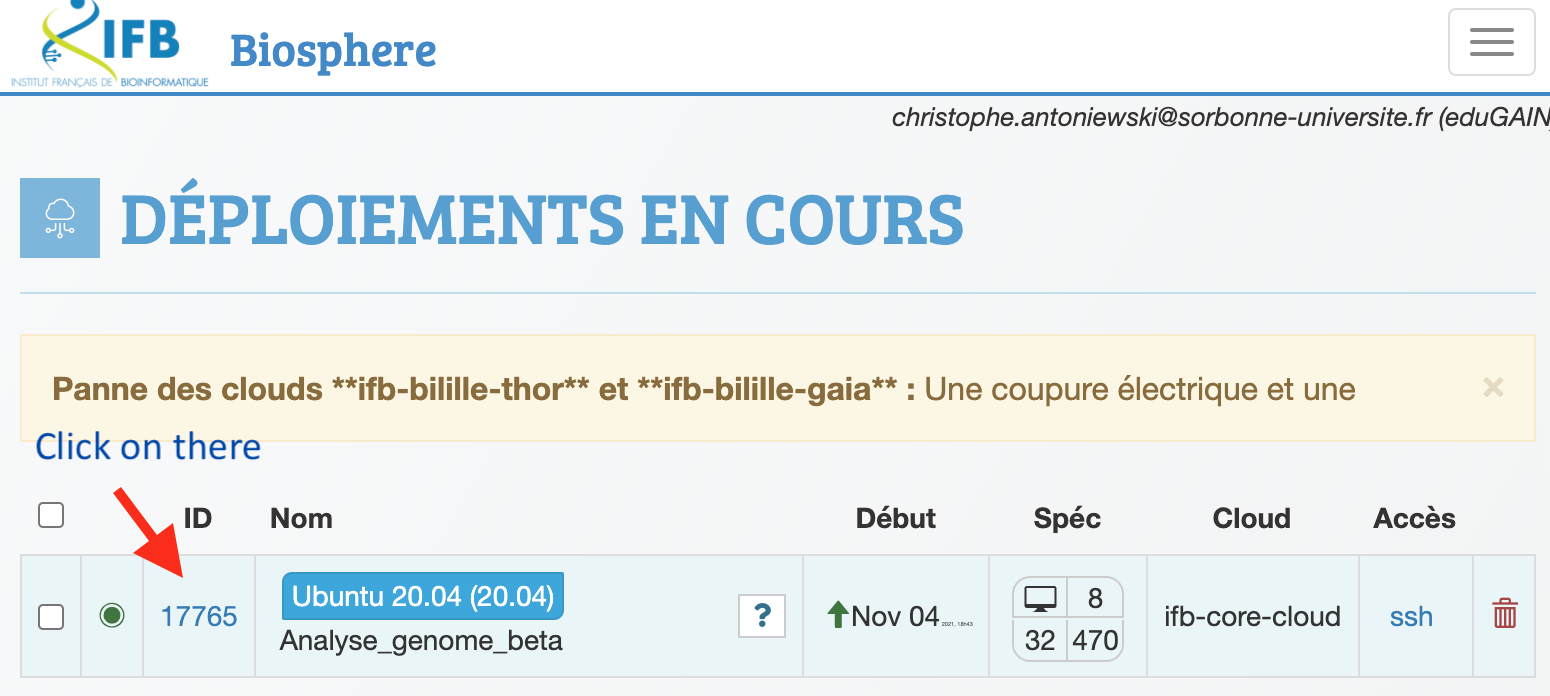
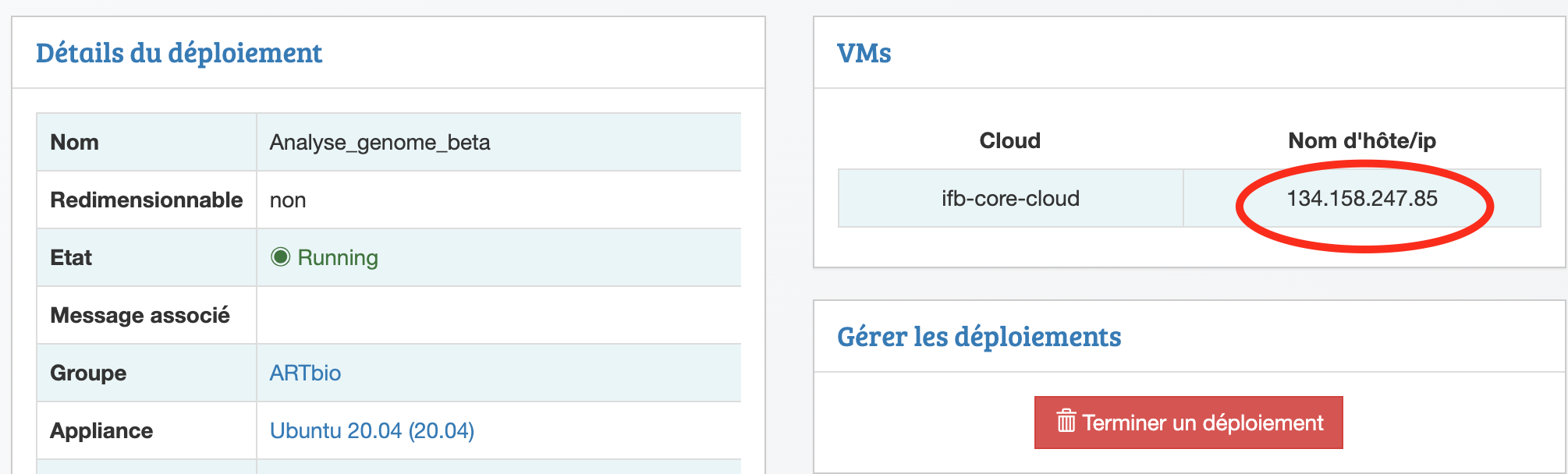
This IP address is available at the IFB biosphere interface
2. Tunnelling the unaccessible port 80 through an accessible ssh (22) port¶
Using this method, no need to set network parameters for your system or in your browser.
Type the following command in a terminal window, and leave it alive:
sudo ssh -A -N -L 80:<your.ifb.cloud.ip>:80 ubuntu@<your.ifb.cloud.ip> # replace <your.ifb.cloud.ip> by a real ip address
# warning: the asked password in the one for the sudo command, ie, your admin password for your local machine, if you know it
OR, if it does not work
Type the following command in a terminal window, and leave it alive:
sudo ssh -i .ssh/<your_ifb_private_ssh_key> -N -L 80:<your.ifb.cloud.ip>:80 ubuntu@<your.ifb.cloud.ip> # replace <your.ifb.cloud.ip> by a real ip address
# warning: the asked password in the one for the sudo command, ie, your admin password for your local machine, if you know it
# <your_ifb_private_ssh_key> is a file located in the ~/.ssh folder, which you should have generated at your IFB cloud registration
# warning: this is not the corresponding public key which has the extension .pub (your_ifb_private_ssh_key.pub)
THEN
Access your cloud Galaxy server by typing in your browser http://localhost:80
Note that this address is different from the one used when setting a SOCKS proxy.